Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirota, Yuki*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Kawabata, Takashi*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuo, Yasumitsu*
Bioengineering (Internet), 10(5), p.622_1 - 622_17, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology) dynamics in the H
dynamics in the H conductors LaH
conductors LaH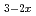 O
O
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Fukui, Keiga*; Iimura, Soshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Tada, Tomofumi*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Kuramoto, Yoshio*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Yamada, Takeshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.184114_1 - 184114_8, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hirota, Yuki*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Kawabata, Takashi*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuo, Yasumitsu*
Bioengineering (Internet), 9(10), p.599_1 - 599_17, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.07(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)Furuike, Yoshihiko*; Ouyang, D.*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito*; Mukaiyama, Atsushi*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Fujiwara, Satoru*; Akiyama, Shuji*
Communications Physics (Internet), 5(1), p.75_1 - 75_12, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:65.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Tominaga, Taiki*; Sahara, Masae*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamada, Takeshi*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 54(6), p.1631 - 1640, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:54.54(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)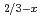 Li
Li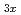 TiO
TiO (x = 0.13) studied by quasielastic neutron scattering
(x = 0.13) studied by quasielastic neutron scatteringMatsuura, Masato*; Fujiwara, Yasuyuki*; Moriwake, Hiroki*; Ohara, Koji*; Kawakita, Yukinobu
Physical Review B, 104(9), p.094305_1 - 094305_7, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Tahara, Shuta*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Maruyama, Kenji*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011071_1 - 011071_6, 2021/03
CuI is a well-known superionic conductor in a high temperature solid phase where the mobile cations migrate between interstitial sites in the f.c.c. sublattice formed by iodine ions. Even in the molten state, it shows several features suggesting collective or cooperative ionic motion. MD results show that Cu diffuses much faster than I. The Cu-Cu partial structure factor have a FSDP which indicates a medium-range ordering of Cu ions. Moreover the Cu-Cu partial pair distribution deeply penetrates into the nearest neighboring Cu-I shell. To reveal origin such anomalous behaviors of molten CuI, we performed quaiselastic neutron scattering (QENS) by the disk-chopper spectrometer AMATERAS at MLF, J-PARC. To interpret the total dynamic structure factor obtained from coherent QENS, the mode distribution analysis was applied. It is found that the motion of iodine is a kind of fluctuating within an almost local area while Cu ions diffuse much faster than iodine ions.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*
Hamon, 29(2), p.91 - 94, 2019/05
Bismuth (Bi) has a double-layered structure based on Peierls distortion in crystalline phase. Complicated static structure in liquid phase which cannot be interpreted by a simple packing model has been conjectured that Peierls distortion may remain even in liquid phase. We measured quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) of liquid Bi by using AMATERAS installed at BL14 beamport of Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC and analyzed coherent QENS spectra. A time-space correlation function revealed that the nearest neighboring shell followed by a shoulder-like structure at longer side consists of four contributions of short and long correlations with relatively long relaxation time of a few tens pico second and medium-ranged and the longest correlations with a short relaxation time of sub-pico second, which is a direct observation of the existing layered structure in liquid Bi. In this article, we report the above scientific results and the method to analyze coherent QENS by the time-space correlation function.
Kofu, Maiko; Faraone, A.*; Tyagi, M.*; Nagao, Michihiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
Physical Review E, 98(4), p.042601_1 - 042601_6, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.09(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Arata, Toshiaki*; Oda, Toshiro*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Fujiwara, Satoru
Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports (Internet), 6, p.220 - 225, 2016/07
Koizumi, Satoshi
Journal of Chemical Physics, 107(2), p.603 - 612, 1997/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.59(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Fujiwara, Satoru; Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru
no journal, ,
Fujiwara, Satoru; Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawakita, Yukinobu
no journal, ,
At J-PARC, AMATERAS and DNA are frequently used for QENS measurements. The former is the direct geometry inelastic neutron spectrometer with pulse-shaping and monochromating disk choppers which enable us to access a wide range of incident neutron energy from 1 to 80 meV. The multi Ei method is very useful for catching overall features from slow and large-scale dynamics to fast and atomic-scale dynamics simultaneously. The latter is the near back-scattering inelastic neutron spectrometer with a pulse-shaping chopper and Si111 analyzer mirrors which enable us to access energy transfer range of -500 to 1500 micro eV with high resolution of 2.4 micro eV. The extremely high signal-to-noise ratio extends QENS and INS applications widely. My talk consists of three parts. (1) Current status of MLF, J-PARC, (2) QENS study of functional materials, and (3) reduction of time-space correlation function of liquid metal.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Tahara, Shuta*; Maruyama, Kenji*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Chiba, Kaori*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have performed coherent quasielastic neutron scattering experiment for liquid polyvalent metals which has complicated static structure not reproduced by a hard-sphere packing model, by utilizing AMATERAS spectrometer in J-PARC. It has been considered that, for Bi and Sb, a double-layered structure originated from Peierls distortion which is seen in solid crystalline phase remains even in their liquid phases. We have succeeded in detection of such Peierls distortion structure in liquid by difference in structural relaxation time at corresponding charateristic interatomic distances in the deduced time-space correlation function.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Tahara, Shuta*; Maruyama, Kenji*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Chiba, Kaori*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed analysis method to reduce the so-call van Hove function, a time-space correlation function, through the regularization method for coherent quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) of liquids. In principle, the van Hove function in r-t space can be obtained by double Fourier transform from dynamic structure factor in Q-E space. Instead of a direct function estimation of the van Hove function through the regularization method which easily involves systematical deviation of the calculated dynamic structure factor from the experimental dynamic structure factor, we used a mediation function between them and estimated it through the regularization method. We will discuss with the properties of the mediation function and the obtained van Hove function and the calculated dynamic structure factor with an example of liquid metals with complex static structure such as Bi and Sb whose QENS were measured by AMATERAS spectrometer in J-PARC.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Matsuura, Masato*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Kofu, Maiko; Tahara, Shuta*
no journal, ,
Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at J-PARC gives opportunities to use pulsed neutron beam to material science including fast ionic diffusion phenomena. DNA and AMATERAS spectrometers in MLF are quite useful to study atomic diffusion directly by quasielastic neutron scattering. We will focus relatively new analysis and experimental methods in this presentation such as mode distribution analysis and deduction of time-space correlation function which are both model free analysis, and possibility to detect an ionic channel in single crystal, with a few examples.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Kobayashi, Makoto*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
The ToF back scattering spectrometer, DNA, installed at the BL02 of MLF in J-PARC, is a tool for quasi-elastic and inelastic neutron scattering. DNA is a unique back-scattering spectrometer with a pulse shaping chopper with maximum rotation speed of 300 Hz. After scattered by the measuring sample, neutrons only with 2.08 meV are selected by Si111 analyzer mirrors. High efficiency and high signal-to-noise ratio are achieved to detect weak signals in inelastic energy region by analyzer mirrors coated with a Gd neutron absorber on the rear of a Si wafer. The subjects of DNA are atomic and spin dynamics ranged from pico to nano second order in bio-molecules, softmatters, and solid state materials such as ionic conductors including batteries and strongly-correlated electron system. In this presentation, in addition of specification of DNA spectrometer, grade-up activities including commissioning work of new analyzer mirrors Si311 and so on will be introduced.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Kobayashi, Makoto*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
The ToF back scattering spectrometer, DNA at BL02, MLF, J-PARC, is a tool for quasi-elastic and inelastic neutron scattering studies aiming at atomic and spin dynamics ranged from pico to nano sec in bio-molecules, softmatters and solid state materials such as ionic conductors including batteries and strongly-correlated electron system. High signal-to-noise ratio are achieved by Si analyzer mirrors back-coated with a Gd neutron absorber. DNA equips a pulse shaping chopper of max 300 Hz and Si111 analyzer mirrors which select the scattered neutrons only with 2.08 meV with the Bragg angle of 87.5 degree and cover a momentum transfer from 0.08 to 1.9 (1/A). Recently we start installation of Si311 analyzer mirrors too which select a scattered neutron with 7.64 meV and widen a momentum transfer range up to 3.79 (1/A). In this presentation, we introduce the spec of DNA including recent commissioning for Si311 analyzer mirrors and several applications to materials science.
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Nakagawa, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English